The Spatial Layer of Material Superphysics
Table of Contents
Descartes is among the first of the moderns who took away the boundaries of the Universe.
Adam Smith
History of Astronomy, Part 9
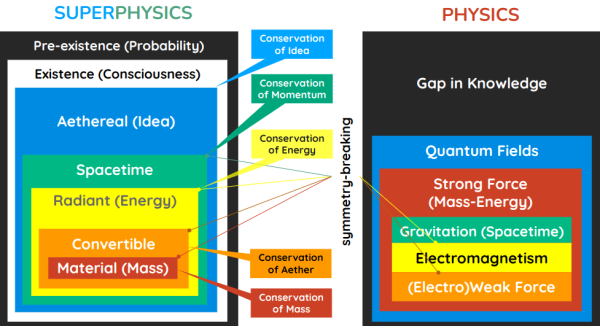
The spatial layer is below the aethereal, as the ‘container’ of reality.
| Attribute | Quality |
|---|---|
| Name | Spacetime |
| Physics Name | Spacetime |
| Traditional Name | Air, Vayu, 木 |
| Descartes’ Name | 2nd Element |
| Domain | Physical |
| Force | Dynamism, Gravity |
| Medium | Gravity Particles (most3) |
| Substance | Space and Time |
| Quanta | Spatial Vortices (qosts) |
| Aether Content | 4 |
| Movement | Purely Kinetic |
| Quality | Subtle, Controls physical reality as the speed of light |
Definition and Properties of The Spatial Layer
The Spatial Layer is where perceptions, such as physical reality, take place.
Unlike the aethereal layer which is only quasi-physical, spacetime is both quasi-physical (via timespace) and physical (via spacetime).
Each particle in the Spatial Layer is made up of 4 aether particles.
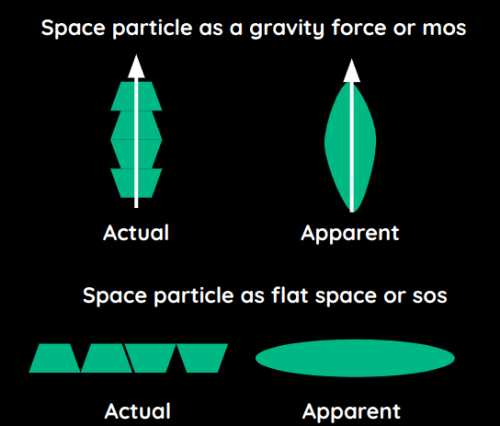
It is purely kinetic energy and has no static forms*. Rather, the relatively static forms of spacetime manifest as the lower layers.
- Parts that have low kinetic energy or aether manifest as empty space or a vacuum
- Parts that have high kinetic energy or aether manifest as vortices. This is similar to a hurricane
Since the Spatial layer is purely kinetic then spatial forces and particles (as media and quanta) are interchangeable.
*The static form as aetherspace in the nucleon of an atom is technically more attached to the Material Layer more than to the Spatial.
The Spatial layer leads to spacetime and sets the speed of light, since it is superior to the 3 lower Layers of:
- Electromagnetism or Radiant Layer
- Weak Force or Convertible Layer
- Strong Force or Material Layer
This layer gives the properties of size, space, timespan, etc the universe and everything in it.