The Shapes of the Particles
Table of Contents
Superphysics sees ideas as static metaphysical objects that have a certain geometry . This was what Euclid’s Element was all about:
Shallow people, of course, judge with their eyes and see that Euclid was explaining shapes and so they think his book was about shapes.
These 3 authors were writing about the 5 Elements:
- Euclid
- Kepler
- Descartes
By combining their principles and merging them with those of Taoism and Hinduism, which learned of the 5 Elements earlier than the Europeans, we can create the following shapes for the particles in Material Superphysics.
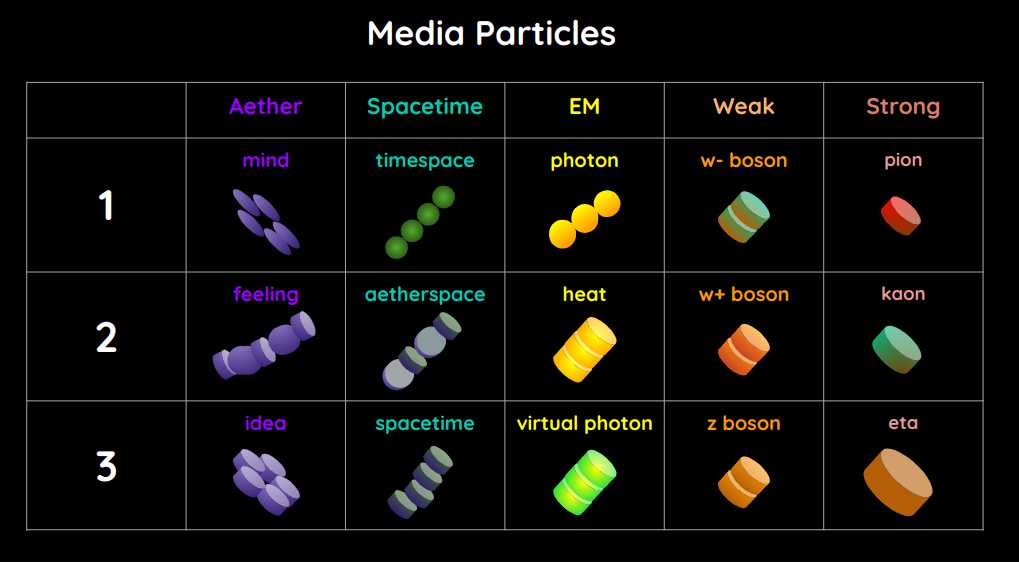
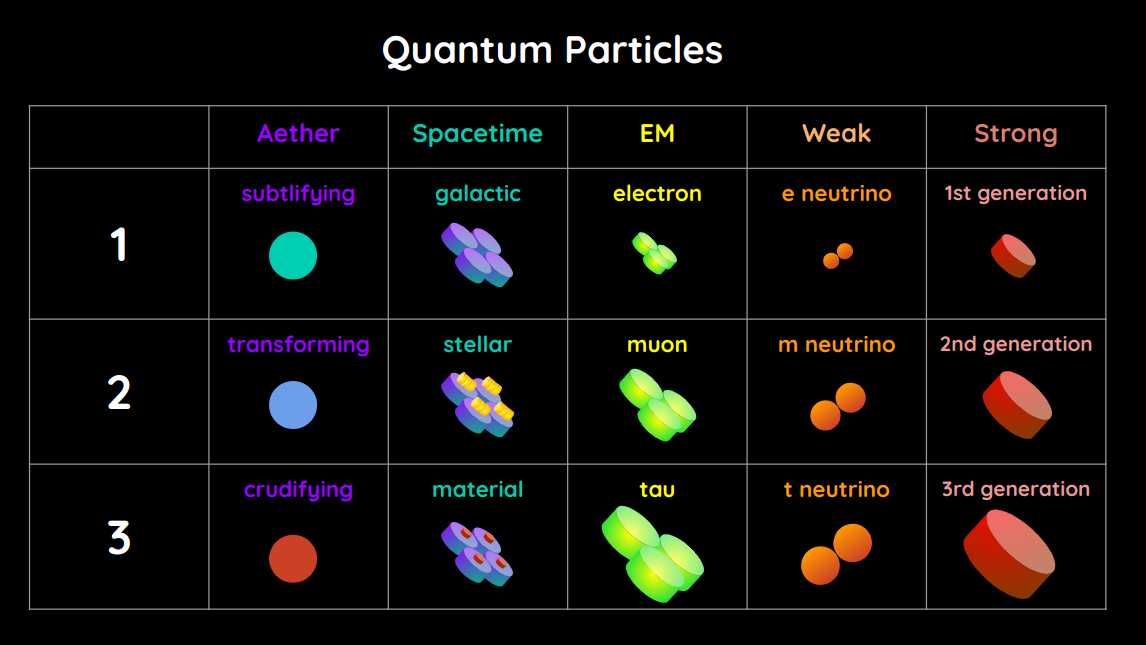
How We Got These
We derived these shapes after listing down:
- The steps in our theory of how the Supreme creates reality in real time
This is the creation of particles of downgrade from idea to matter.
- The effects of the Radiant layer particles namely the photon (light) and virtual photon (magnetism)
This is how the particles interact.
- The steps of particle decay from collisions
This is the decay of particles or upgrade from matter back to the aether.
Some of these particles do not exist in Physics which only knows 3 of the 5 Elements.
This visualization will help us intuitively think of particle interactions.
For example, there is currently a mystery why there is a discrepancy between the predicted mass of the W boson and the actual measured mass.
Our shapes system gives a clue that the culprit is in the neutrinos. This is because in our classification, neutrinos are in the same Layer as the W Boson, but have a flat shape.
How it Works
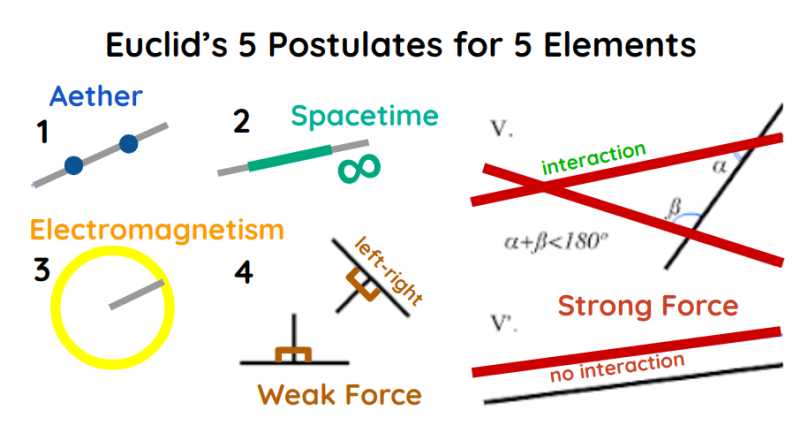
The Euclidean Postulates can be suummed up in a few words:
- Point to Point
We interpret this as the aether particle.
- Infinite Line
We interpret this as the finite aetherspace that can extend indefintely.
- Circle
We interpret this as the “round” action of photons which are shaped as circle in a line.
- Right Angles
We interpret this as the left and right handed spin of the Weak Interaction
- Meeting at a Point
We interpret this as the triangle created by gluon flux tubes (3 aetherspace particles).
Each quantum particle is made up aether particles which can either be:
- round
- flat
They are small columns, hollowed out with 3 spirals like screw-threads. This lets them pass through those narrow passages while twisting
Rene Descartes
Principia Philosophia, Part 3, Article 87
These particles can be arranged in 2 ways:
- as a plane structure
- as a column structure
Force particles are generally tall because this gives them power to bore through other particles.
Matter particles are generally shaped into a plane so that they can receive the force particles.
| Physics Name | Superphysics Version |
|---|---|
| Magnetic Moment | Size of Hole of Charged (or Gendered) Particle |
| Charge | Rotation Direction |
| Male Charge | Rotating Positively or Anticlockwise |
| Female Charge | Rotating Negatively or Clockwise |
| Spin | Orientation to Virtual Photon (means particle has thickness). A + spin means |
| Electromagnetic Mass | Size (or Thickness?) of Hole to use Virtual Photons |
| Material Mass | Aetherspace Strength |
Why Use Particle Shapes?
Particle shapes remove the need for Feymann diagrams. This is because Feynman used action principles to trace paths in quantum mechanics.
However, Descartes’ Physics uses vortices wherein spin is more important than paths. Rather, the path is the effect of the spin. This is how meteorologists plot typhoon movement from their eye.