The Fourth Branch of Government
Table of Contents
Ever since the French Revolution, there have been three branches of government:
- Legislative - this branch is the most important branch as it creates the laws
- Executive - this branch executes laws and is the most visible one
- Judicial - this branch settles legal conflicts
If we view society as a family and the government as the parents, then the legislative and executive are the father, while the judicial is the mother. The former requires wisdom and intellect, while the latter requires love and conscience. As you can see, the two fatherly branches of the government outweigh the single motherly branch.
This is why, although there might be legal justice, there is little avenue for political or economic justice. This is seen in the election of corrupt officials and in the presence of economic inequalities.
The Resources Branch
To complete the proper system of government, Supereconomics proposes a Resource branch to be the fourth independent branch of government. This will mimic the role of a housewife in budgeting the family’s expenses and in noting down the needs and condition of each child, which represents each citizen or group of citizens.
At the moment, such responsibilities are done by the Audit and Budget department or Treasuries of governments. These are usually as a separate statutory body or constitutional commission, which merely acts as an appendage instead of being an equal to the three branches.
- The expertise of the executive branch is physical action.
- The expertise of the legislative branch is debate and legal experience.
- The expertise of the justice branch is jurisprudence.
- The expertise of the resource branch is the inspection and aggregation of real data and its real-world presence.
The legislative makes a law and allocates the budget. The resource branch does the sourcing and prepares the allocation. The executive uses those resources to implement the law. The resource branch then audits the executive and sends the cases to the judiciary.
The main duties or the resources branch will be:
- checking that all accounts of governments are in order, that all projects have their proper funds and resources in order to prevent costly delays and overruns
- checking the material condition of the people to ensure that economic justice is administered, or that the resources are going to the right recipients and being used efficiently
- handling the logistics for the system of barter tax farming
- to handle the government’s welfare department by redistributing goods and services to the needy
- to monitor the other branches of government to see it they are amassing wealth at the expense of others
- to monitor the morality level of other branches, including the applicants to them, to show whether such branches and candidates are moral or not. For example, it can proactively initiate action in the legislative to investigate abuses by the executive, and vice versa
Black/white above represents Yang-yin. Four colors below represent Four Laws of value and four classes
| _ | Father | Father | Mother | Mother |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Branch | Legislative | Executive | Judicial | Resources |
| Task | Makes laws, Does the research | Implements laws, runs the army | Tries cases according to the law | Sources and coordinates resources |
| Skillset | Rhetoric, Research | Leadership, Governance | Attention to detail, Diligence | Morals, Experience |
The resources branch takes away some of the motherly duties such as caring for the poor and arranging for the logistics of supplies, away from the father, or the executive. In this way, the father can focus on more important things. This branch is independent like the others. But while the executive and legislative are elected, the manpower for the judicial and resource branches are sourced from law schools and accounting or econometrics schools.
The British Exchequer is similar to the resources branch:
The present revenues consist chiefly of.. the funds mortgaged for paying off the public debts. Examples are taxes on salt, beer, malt, etc., levied by the officers of custom and excise. These cannot be touched by the king as they are paid to the court of exchequer. The exchequer is generally managed by people of interest and integrity. They have their offices for life and are quite independent of the king. They can pay only to those appointed by parliament.
Adam Smith
The Lectures on Jurisprudence
A Sample Implementation
In the current system:
- The legislature creates a new tax
- The tax will be collected by the executive
- Tax cases will be tried by the executive or judiciary
In the proposed system:
- The legislature creates a new tax
- The resource branch will show how and where it will be extracted from, together with projections on its effects
- The ironed-out plan will then be sent to the executive for implementation
- Anomalies in tax collection will be exposed and tried by the resource branch, with the judiciary supporting or overturning the judgment
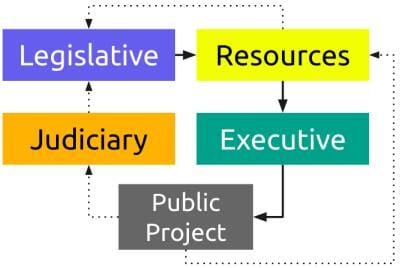
This will ensure that every budget is realistic and every project or service can be implemented within the planned period. In the current system, many projects are delayed or not implemented because the budget is only good on paper.
How It Could Have Been Implemented
As a historical example, let us put ourselves in the American Revolution in 1777 at Valley Forge.
At that time, George Washington (executive branch), could not get food for his troops because the expertise of Congress (legislative branch) was lawmaking and not logistics. A resource branch of government would’ve mapped the resources available in the colonies in advance and then relay the information to the executive for collection. Any injustice committed would then be tried by the judicial branch.
The idea for this branch came up while planning out the implementation of our new economic system in an actual society. Since we don’t have much manpower, we tried to automate, or at least make the system automate-able in the future.
The resources needed to run the system have to be used as efficiently as possible without an expensive adminstrative system. Thus, the idea for an automate-able resource branch came about, which will have its genesis as the resource banking system (which we call points banking) used to safeguard all transactions.
This is in line with both the vision of economic singularity and David Hume’s Ideal Commonwealth