Four Wave Properties: Commonality, Density, Strength, Spread
Table of Contents
| Principles | Concepts Introduced |
|---|---|
| Four Wave Properties: Commonality, Density, Strength, Spread |
The previous section explained how Existence is formed from waves in abstract spaces. This creates the current universe that is wave-based, as proven by:
- electromagnetic waves
- gravitational waves
- gluon field in matter moving like waves
- baryonic acoustic oscillations
- people with the same personality (mental vibration) being friends
- etc
The laws of Nature, from thermodynamics, the stages of life, and social cycles all show the wave properties of Existence which we can distill into 4:
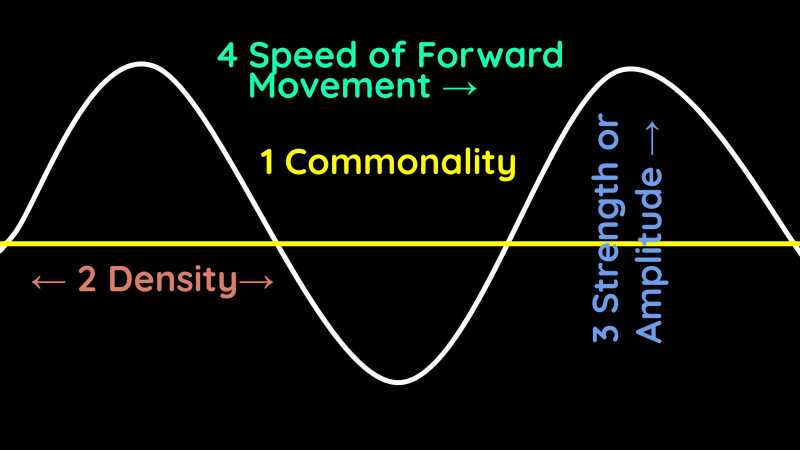
- Continuous Commonality
A metaphysical wave stretches is continuously like a line. This is different from a dot which is finite.
This is why we say that the universe had no beginning and therefore no end.
- Frequency or Density
There are many waves in Nature. These can be bunched up creating more density and a richer Existence, or loosely spaced creating a blank Existence.
- Strength or Amplitude
A wave can have high amplitude as being loud and energetic, or a low amplitude as quiet and low energy.
- Spread or Forward movement
A wave is a disturbance in a line that can travel fast or slow depending on its energy relative to external energies or other waves.
These 4 properties manifest as the laws and rules in Nature which we can distill as: commonality, density, strength, and speed.
The 4 Rules of Motion in all Sciences
Movement in physical space comes from space particles of the Air Element which Material Superphysics calls the Spatial Layer. Since space is made up of waves, as seen in gravitational waves, then the 4 properties of waves manifest as the 4 Rules of Motion as explained by Descartes and Spinoza.
Rule 1: No Void
No identity moves into the place of another body unless at the same time that other body moves into the place of another identity.
This is the most important rule as it also manifests in Biology.
Rule 2: Straight or Circular
Every moving identity moves in a straight line when alone, and in a curve or a circle when moving with others. When in a circle, it moves away from the center.
Rule 3: Collisions
When a weaker identity hits a stronger, it will be deflected. When a stronger hits a weaker, it will transfer some of its force to the weaker
Rule 4: State Continuity
Each identity remains as much as it can always in the same state. It is never changed except by external causes.
The 4 Rules of Conversion
This implements the Law of Conservation of Aether to be discussed in Chapter 5f.
- Mass Balance
Conversion involves material particles, not energy or space particles.
- Force Carrier or Enzyme Specificity
Every step is mediated by a specific force carrier or enzyme.
- Allosteric Regulation
Molecules bind to enzymes or force carriers to speed up or slow down the conversion process.
- Exergonic Movement
Every reaction must release Radiant energy.
The 4 Rules of Stoichiometry
This implements the Law of Conservation of Mass to be discussed in Chapter 5f.
- Definite Proportions
A specific chemical compound always contains its component elements in fixed ratios by mass, regardless of the compound’s source or method of preparation.
- Multiple Proportions
When 2 elements combine to form more than 1 compound, the masses of 1 element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in a ratio of small whole numbers.
- Reciprocal Proportions
This is when 3 different elements combine.
- Gay-Lussac’s Law of Gaseous Volumes)
When gases react, the ratio of the volumes of the gaseous reactants and products (measured at the same temperature and pressure) are in a ratio of small whole numbers.
The 4 Laws of Thermodynamics
We rearrange the law of thermodynamics to match the 4 properties of waves
1. Temperature (0th Law): Common Thermal Equilibrium
2. Conservation (1st Law): Energy changes forms
3. Absolute Zero (3rd Law): No radiation at absolute zero
4. Entropy (2nd Law): Hot radiates to Cold
This will be explained in Material Superphysics
The 4 Stages of Life
This is called Ashrama Dharma in Hinduism which we apply to all organic life and will be explained in Bio Superphysics.
1. Childhood
This is the lag phase for organisms, as seen in bacteria, as they adjust to their new environment
2. Adolescence
This is the rapid growth stage after the organisms after they adjust to their environment
3. Adulthood
Growth slows down
4. Old age
Organism declines as its spirit moves on
The 4 Races
- African
- Aryan
- Mongolian
- Austric
These are the names of the first men created:
- Balam-Quitzé
- Balam-Acab
- Mahucutah
- Iqui-Balam
Kiche People
Popol Vu, Part 3, Chapter 2
The 4 Social Cycles of Socrates
This is the same as the Varnashrama system in the Vedas except that they are dynamic and not static.
1. Worker (Democrat or Liberal)
The society starts, requiring hard work
2. Warrior (Tyrant or Military)
The society gets strong leadership and stabilizes.
3. Thinker (Aristocracy or Intellecuals)
The society develops its civilized culture and philosophies.
4. Trader (Oligarchy or Merchants)
The society gets rich through trade and soon degenerates.
These will be explained by Social Superphysics.
The 4 Laws of Value of Supereconomics
These are based on Book 4 of Adam Smith’s Wealth of Nations where he explains the sustainable flow of capital and wealth.
1. Everything has Value (Worker)
Violations of this law lead to the Poverty Cycle, inequality, unemployment
2. Value is Created to Remove Lack
Violations of this law lead to Asset price bubbles and job-skill mismatch
3. There must be balance in the creation and spread of value
Violations of this law lead to moral hazard and excess capacity
4. Value is transferred through fair exchange
Violations of this law lead to inflation or recessions.
These will be explained by Supereconomics.
The 4 Laws Branches of Government
These are from the 4 cycles of Socrates which we establish as the 4 branches of government, as an upgrade to the current systems which only have 3 branches. These will be explained by Supersociology.
1. Legislative (Father)
This handles the creation of the laws according to the Constitution
2. Executive (Father)
This handles the execution of the laws
3. Judicial (Mother)
This is settles the interpretion of the laws.
4. Resource (Mother)
This is handles the budget and allocation of resources.
The 4 Spiritual Paths
These are the 4 ways towards the Absolute Entity via the Supreme Entity. These will be explained by Spiritual Superphysics.
1. Karma (Action)
This is experiencing the Supreme through action and reaction
2. Raja (Discipline)
This is experiencing the Supreme through rigid discipline and austerity
3. Jnana (Intellect)
This is experiencing the Supreme through intellect, research, and reasoning
4. Bhakti (Devotion or Love)
This is experiencing the Supreme through devotion and love.
We can summarize these as follows:
| Property | Motion | Heat | Life | Economy | Govt | Spirit | Races |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commonality | No Void | Temperature | Child | Nominal | Legislative | Action | African |
| Density | Spin | Conservation | Adolescent | Real | Executive | Discipline | Aryan |
| Strength | Collision | Zero | Adult | Natural | Judiciary | Intellect | Mongolian |
| Spread | Inertia | Entropy | Elderly | Market | Resources | Love | Austric |