Use Value and Marginal Utility
Table of Contents
Principles
| Principles | Assertions |
|---|---|
| Use Value requires 1 entity | We replace Marginal Utility with Minimum Needs since use-value is subjective |
In Neoclassical Economics, the use-value is called ‘utility’ and is the foundation of its theories like marginal utility.
According to Economics, utility is the satifaction that you get from a good or service.
Initially, this satisfaction increases with every additional item bought. But in time, your satisfaction from the item increases in smaller amounts until it no longer increases.
This can be seen as gradual Destructive Interference that flattens the desire for that utility.
For example:
- adding a few essential apps on your phone can address your desire for useful tools
- but adding too many apps will occupy disk space and drain battery while adding to information overload
In the latter case, the wave overcorrects and goes beyond flat. It takes an opposite form to the original desire, leading to aversion.
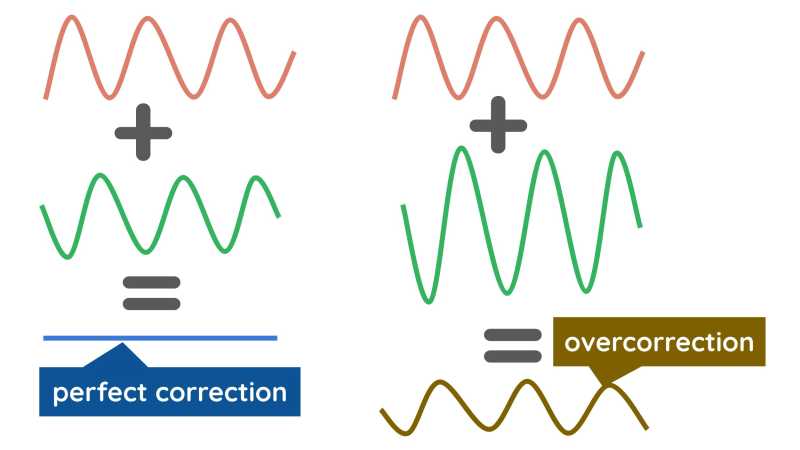
Marginal Utility
Just before the wave goes flat, the utility that you get is “marginal”. This feeling tells you to stop buying since the desire has been satisfied.
This system of marginal utility requires the quantification of pleasure or utility.
- This is then ‘maximized’ as ‘profit maximization’ in Economics.
The problem is that, in the physical domain, objects are finite. So a maximization of objects in one area will lead to a minimization in another.
- This minimization leads to poverty and inequality.
When the maximization is done unnaturally, such as through speculation, the fake maximization will be exposed for its true value which is not so high.
- This leads to as economic crashes.
Supereconomics disregards marginal utility because:
- Use value or utility is just one of the pre-exchangeable values
There are other values like historical value, environmental value, sentimental value, etc.
- Maximization of exchangeable value increases untruth
Utility functions are measured in money which is not exactly the same as the product or service being exchanged. Maximizing a money-based utility function maximizes the untruth.
For example, if you can only eat 5 slices of pepperoni pizza, then your maximized utility is likely at 4 slices.
If 1 slice of pepperoni pizza is $1, then you will conclude that $4 is the optimal money you should bring to the pizza store.
But what if there is no pepperoni pizza available? Or what if the store is closed and you have to go to a sandwich shop instead? Your $4 will not produce the same result.
So marginal utility and maximization are just good in theory and not in practice.
This is why there are so many economic problems in economic systems.
This flaw of Economics comes from the crudeness and oversimplification of mind of the economist arising from the focus on objectivity.
This is fixed by the 1st Law of Value which restores subjectivity through relationality.